CHRONOBIOLOGIE
Ou l’étude des rythmes biologiques
Par le docteur Eric GAEREMYNCK
EPU CALFORMED du 07/10/2004

METHODES D’ETUDE
►
► HYPOTHESE DE DEPART BASEE SUR:
§ EPIDEMIOLOGIE
§ ETUDES ANTERIEURES
§ EXPERIMENTATION ANIMALE (rat)
► ETUDE SUR VOLONTAIRES:
§ CONDITIONS
§ LA DUREE DEPEND DU CYCLE OBSERVE
► EXPERIMENTATION CLINIQUE



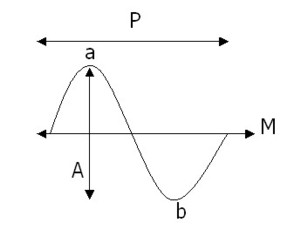
UN CYCLE BIOLOGIQUE EST DEFINI PAR:
– Sa période (P)
– Son acrophase (a): pic
– Sa bathyphase(b) : creux
– Son amplitude (A) : diff. Entre pic et creux/2
– Son mésor (M) : moyenne arithmétique de la totalité
ORIGINE DES RYTHMES BIOLOGIQUES:
– ENDOGENE: GENETIQUE, HORLOGE BIOLOGIQUE
– EXTERNES OU SYNCHRONISEURS:
• Alternance jour/nuit
• Alternance activité/repos
AUTRES: t°, saison, vie sociale…
LES DIFFERENTES PERIODES
ULTRADIENNE (<20h)
§ Exemple: oscillations hormones hypophysaires
CIRCADIENNE (20 à 28h)
§ Exemple: cortisol…
INFRADIENNE (> 28h)
§ Circaseptidienne (7 +/- 3 jours)
§ Circamensuelle (30 +/- 5 jours): menstruel, lunaire
§ Circannuelle (1 an +/- 3 mois)
LES MARQUEURS DE DESYNCHRONISATION
CORTISOL
TEMPERATURE CORPORELLE
MELATONINE
SOMMEIL

CYCLE VEILLE-SOMMEIL
► Un bon exemple de rythme circadien et ultradien largement étudié est celui du sommeil:
- Ultradien: alternance des différentes phases de sommeil selon une période de 90’
- Circadien: période en libre cours (grotte) de 29H « synchronisée » à 24H par l’alternance nuit jour, rythme de vie sociale…
INFLUENCE DE LA T° CORPORELLE
► LE RYTHME DE LA T° CORPORELLE INFLUENCE :
§ LA LATENCE D’ ENDORMISSEMENT
§ LA DUREE TOTALE DU SOMMEIL
§ LA LATENCE ET LA DUREE DES EPISODES DE SOMMEIL PARADOXAL
=> 4x PLUS LE RYTHME DU SOMMEIL QUE L’ INVERSE
§ = OSCILLATEUR FORT
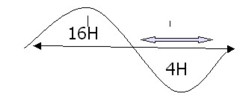
► CYCLES DE SOMMEIL + RAPPROCHES AU MINIMUM THERMIQUE (4H)
=> NOMBRE MAXIMAL DE PHASES DE SOMMEIL PARADOXAL
CYCLE VEILLE-SOMMEIL
► Perturbations de ce cycle:
- Naturelles: ceux du matin, ceux du soir
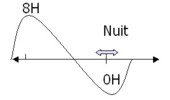
► Étude de familles du soir (décalage du sommeil vers le matin, endormissement tardif): décalage du minimum thermique à 8H (mutation génique)
► Sujets âgés : avance de phase (endormissement devant la télé) à Luminothérapie à 8000lux entre 20H et 20H 30
► Retard de phase: Luminothérapie à 8000 lux le matin entre 8H et 8H30
- Imposées: vols transméridiens, travail posté
VOLS TRANSMERIDIENS (1)
► Minimum 6H de décalage horaire:
§ Inversion du rythme veille sommeil : 3 jours
§ Inversion du rythme de t° : 7 jours
§ Inversion du rythme du cortisol : 21 jours
> DESYNCHRONISATION INTERNE: envies de manger à des heures indues, sensation de froid…= « JET LAG »

TRAITEMENT : RESYNCHRONISATION EXTERNE:
Soleil, activité sociale, activité physique
MELATONINE: 5mg vers 17-18h et non au coucher (5h avant sécrétion de mélatonine)
LUMINOTHERAPIE: +++
¤ Naturelle: exercice physique en milieu de journée (lumière la plus intense)
¤ Artificielle: 5OOO -10000LUX sont nécessaires pour bloquer la sécrétion de mélatonine
à Voyage à l’est: lumière le matin (retard de phase)
à Voyage à l’ouest: lumière le soir (avance de phase)

Exemple d’ appareil de luminothérapie

Extrait de « esprit femme », journal féminin